Deploy a Laravel project to ECS using Fargate
This article explains how to deploy a Laravel project to Amazon ECS on AWS using Fargate.
Reference
- Pushing a Docker image to an Amazon ECR private repository
- Learn how to create an Amazon ECS Linux task for the Fargate launch type
- Amazon ECS task execution IAM role
- Amazon ECR interface VPC endpoints (AWS PrivateLink)
Prerequisites
- An AWS account
- A user in IAM Identity Center
For more information, follow this instruction. - AWS CLI already installed
For more information, follow this instruction - An SSO session and a profile with AWS CLI
For more information, follow this instruction
Environment
- Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS (running on WSL)
- Docker Engine 26.0.0
- Laravel 11
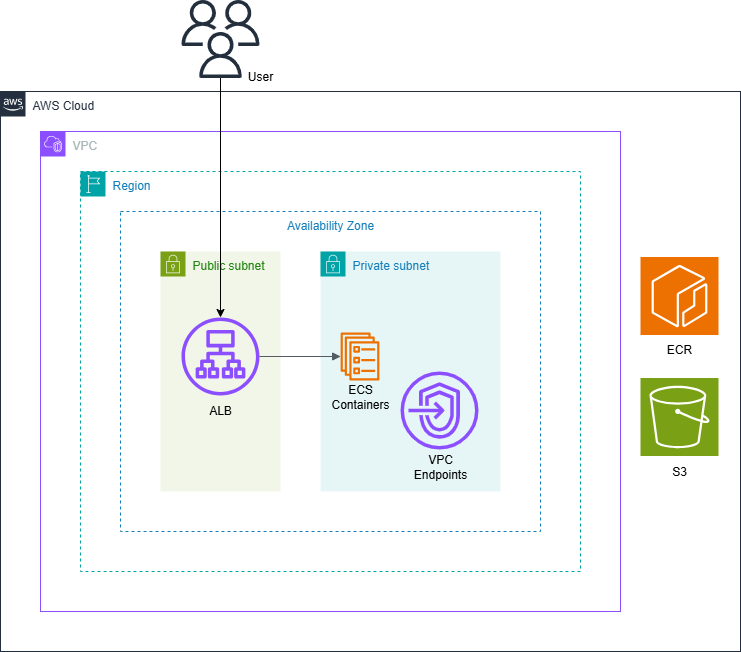
Architecture Diagram
This is an architecture diagram for the system we’ll build.
Deployment Steps
- Create Laravel Project
- Create Repository
- Push Docker Image
- Create Cluster
- Create ECS Task Execution IAM Role
- Create Task Definition
- Create Security Group
- Create VPC Endpoints
- Create Application Load Balancer
- Create Service
- Verify Laravel Project
1. Create Laravel Project
Create a Laravel project.
For more information, refer to this article.
If you use the above example, modify the Dockerfile as follows:
(Add a process to copy the project sources into the container and adjust paths when copying files)
Dockerfile:
FROM amazonlinux:2023
# (Added) Copy this project source to the container
COPY . /srv/example.com
# (Changed) Adjust paths when copying the files
# e.g., nginx/nginx.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo -> docker/web/nginx/nginx.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
# Install NGINX
RUN yum -y install yum-utils
COPY docker/web/nginx/nginx.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
RUN yum -y install nginx-1.24.0
COPY docker/web/nginx/conf.d/default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
# Install php-fpm
RUN yum -y install php8.2-fpm php8.2-mbstring
# Not creating the directory in advance will cause an error
RUN mkdir /run/php-fpm
RUN mkdir /var/run/php
COPY docker/web/php/php-fpm.d/zzz-www.conf /etc/php-fpm.d/zzz-www.conf
Also modify the docker-compose.yml file if you plan to run the container locally.
Change the path where the container is built and specify the Dockerfile path:
(The container needs to be built in the project root path to copy the sources)
docker-compose.yml:
services:
web:
# Change the "build" field
build:
context: .
dockerfile: ./docker/web/Dockerfile
volumes:
- .:/srv/example.com
ports:
- "8080:80"
command: bash -c "chmod 755 /srv/example.com/docker/web/start.sh && /srv/example.com/docker/web/start.sh"
Please make sure not to include any Git-related files or other files that are unnecessary for the production environment for security reasons.
It’s a good idea to create a .dockerignore file like the following:
.dockerignore:
**.git
**.gitignore
**.gitattributes
**.md
2. Create Repository
Navigate to ECR on AWS Management Console.
Click the “Create” button.

Enter a repository name of your choice and click the “Create” button.
In this example, specify “laravel-project-repository”.
3. Push Docker Image
Build the Docker image with the registry format:
$ docker build -t <Your AWS account ID>.dkr.ecr.<Your ECR repository region>.amazonaws.com/laravel-project-repository .
Specify the -f option if your Dockerfile is not in the project root directory:
$ docker build -t <Your AWS account ID>.dkr.ecr.<Your ECR repository region>.amazonaws.com/laravel-project-repository -f <Your Dockerfile path> .
If you already have a Docker image, retag it as follows:
$ docker tag <Your Docker image repository or image ID>:<Your Docker image tag> <Your AWS account ID>.dkr.ecr.<Your ECR repository region>.amazonaws.com/laravel-project-repository:latest
Authenticate your Docker client with the Amazon AWS ECS registry and run docker login:
$ aws ecr get-login-password --region <Your ECR repository region> | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin <Your AWS account ID>.dkr.ecr.<Your ECR repository region>.amazonaws.com
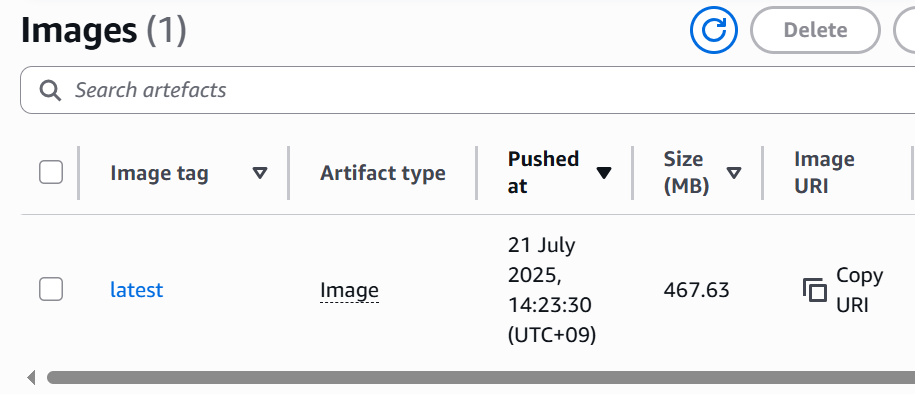
Push your Docker image to your ECR repository:
$ docker push <Your AWS account ID>.dkr.ecr.<Your ECR repository region>.amazonaws.com/laravel-project-repository:latest
You can check your image on Amazon Management Console.
4. Create Cluster
Navigate to ECS on AWS Management Console.
Click the “Create Cluster” button.
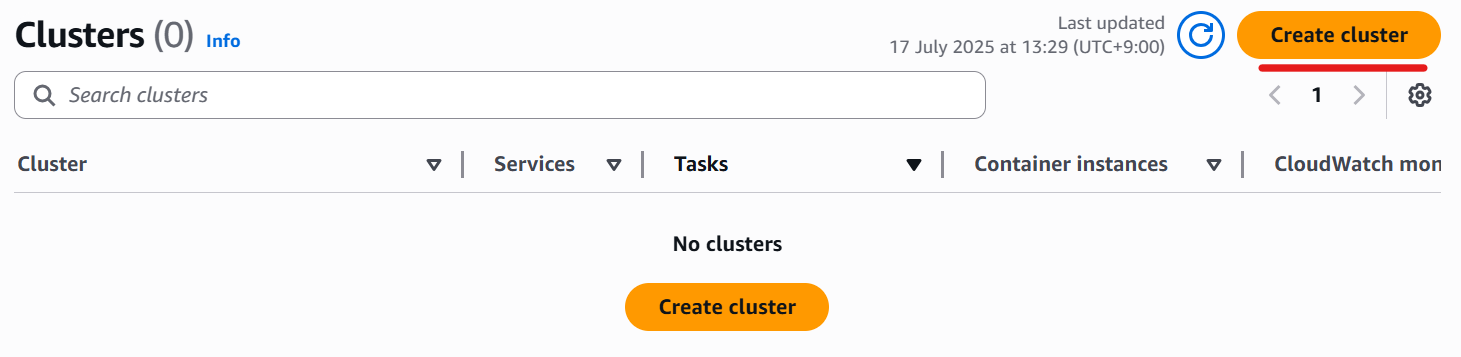
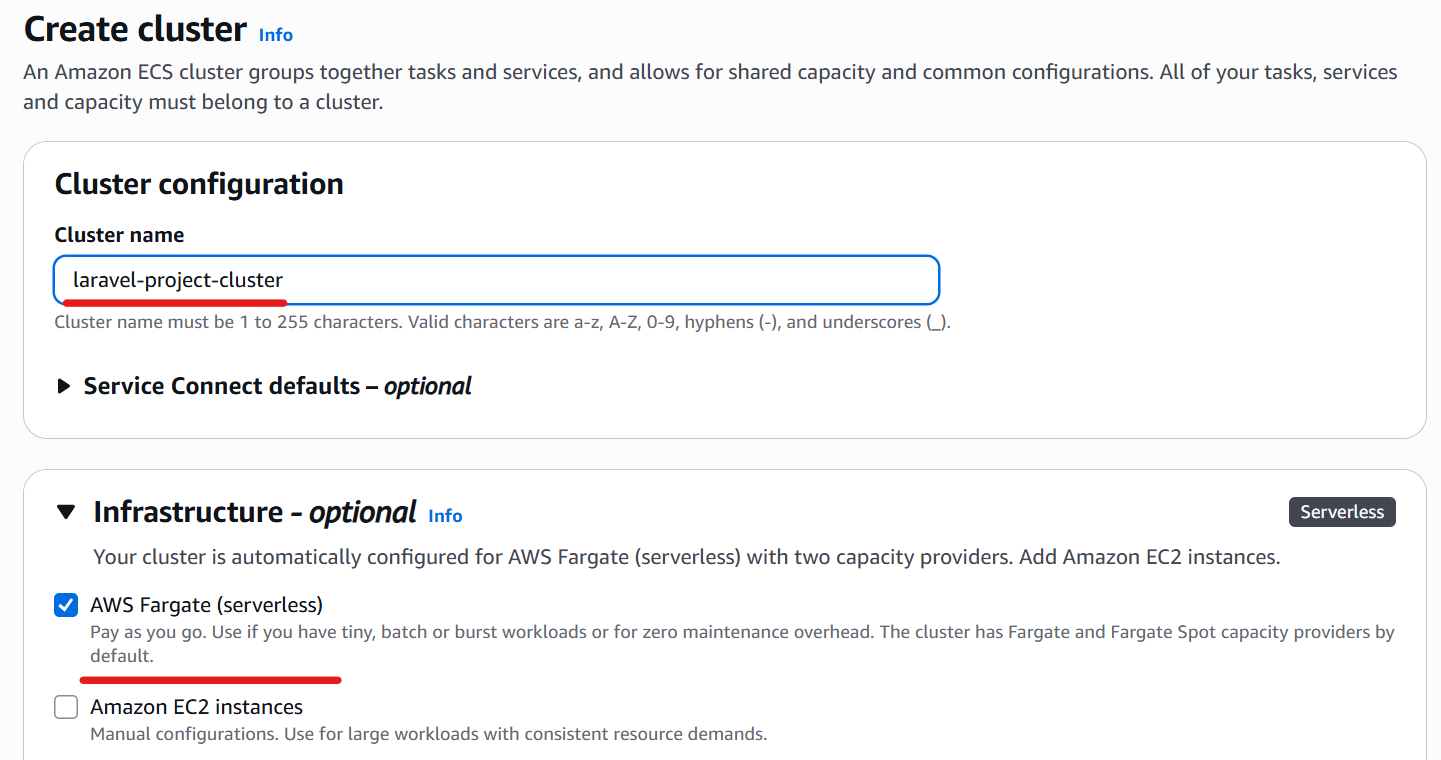
Enter any cluster name and check the “AWS Fargate (serverless)” checkbox.
In this example, specify “laravel-project-cluster”.
Then click the “Create” button.
5. Create ECS Task Execution IAM Role
To grant containers and Fargate agents permission to use AWS services, create an ECS task execution IAM role.
Navigate to IAM on IAM on AWS Management Console and click “Roles”.
Click the “Create role” button.

Select “AWS Service”, then choose “Elastic Container Service Task”.
Click the “Next” button.
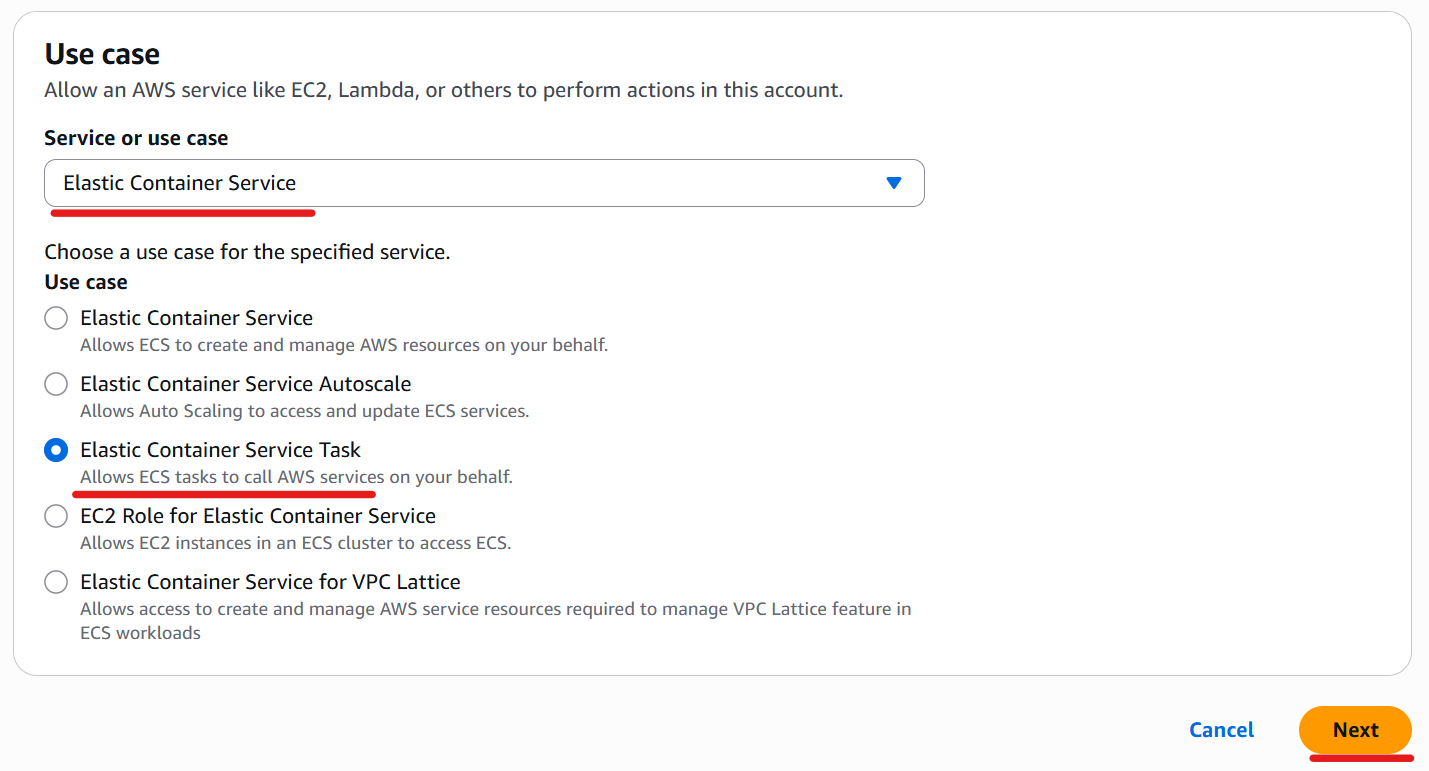
Select the “AmazonECSTaskExecutionRolePolicy” policy.
You can add additional policies as needed (e.g., S3 access if required during container builds).
Click the “Next” button.
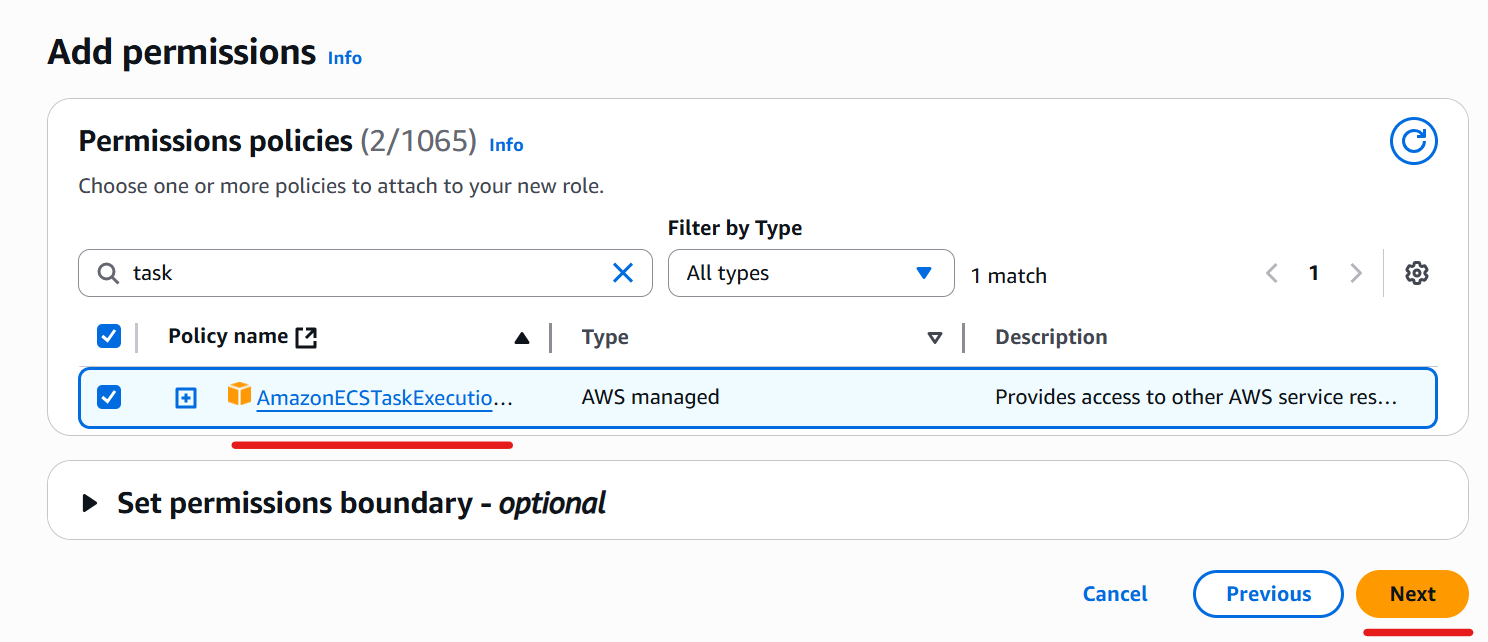
Enter “ecsTaskExecutionRole” in the Role name field (you can choose any name).
Click the “Create role” button.
6. Create Task Definition
A task definition is used to create ECS tasks.
In this example, we’ll create a task definition for this project.
Navigate to “Task definitions”.
Click the “Create new task definition with JSON” option.
Enter any value into “family”(laravel-project-fargate) and “containerDefinitions.name”(web) fields.
Retrieve your image URI and enter it in the “containerDefinitions.image” field.
Add the “portMapping” and “command” items.
task definition:
{
"requiresCompatibilities": [
"FARGATE"
],
"family": "laravel-project-fargate",
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "web",
"image": "<Your AWS account ID>.dkr.ecr.<Your ECS repository region>.amazonaws.com/laravel-project-repository:latest",
"portMappings": [
{
"containerPort": 80,
"protocol": "tcp"
}
],
"essential": true,
"command": [
"/bin/sh",
"-c",
"chmod 755 /srv/example.com/docker/web/start.sh && /srv/example.com/docker/web/start.sh"
]
}
],
"volumes": [],
"networkMode": "awsvpc",
"memory": "3 GB",
"cpu": "1 vCPU",
"executionRoleArn": "ecsTaskExecutionRole"
}
Click the “Create” button.
7. Create Security Group
Go to VPC on AWS Management Console, then click “Security groups”.
Click “Create security group”.
Create the following security groups.
For private
Inbound rules:
| Type | Port range | Source | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| All traffic | All | This security group ID | To access VPC endpoints. |
| All traffic | All | Security group ID for public | To allow the Load Balancer to access ECS tasks. |
Outbound rules:
| Type | Port range | Source | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| HTTPS | 443 | 0.0.0.0/0 | To pull ECR images. |
For public
Inbound rules:
| Type | Port range | Source | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| HTTP | 80 | 0.0.0.0/0 | To allow access to the Load Balancer. |
Outbound rules:
| Type | Port range | Source | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| All traffic | All | Security group ID for private | To allow access to ECS tasks. |
8. Create VPC Endpoints
To pull ECR images from ECS tasks in private subnets.
In this example, the following three endpoints are required.
com.amazonaws.region.ecr.dkrcom.amazonaws.region.ecr.apicom.amazonaws.region.s3(Gateway)
This is because ECR uses Amazon S3 to store image layers.
Go to VPC on AWS Management Console.
Click “Endpoints”.
Click “Create endpoint”.
Enter a name and select “AWS services” for the Type.
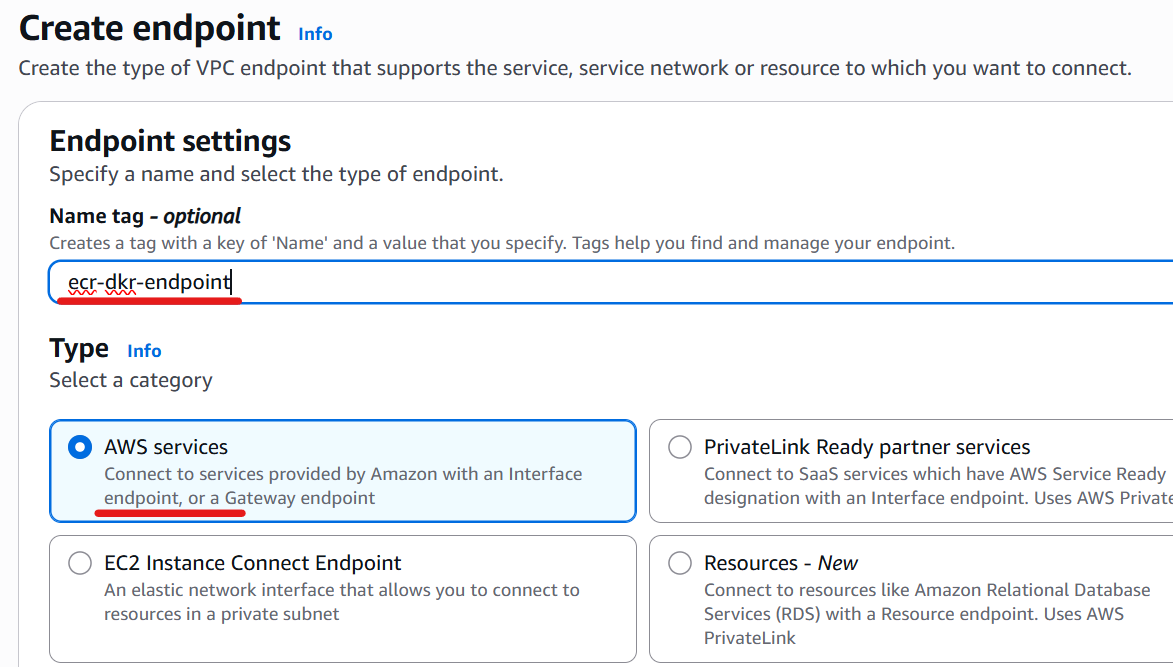
Choose com.amazonaws.region.ecr.dkr.
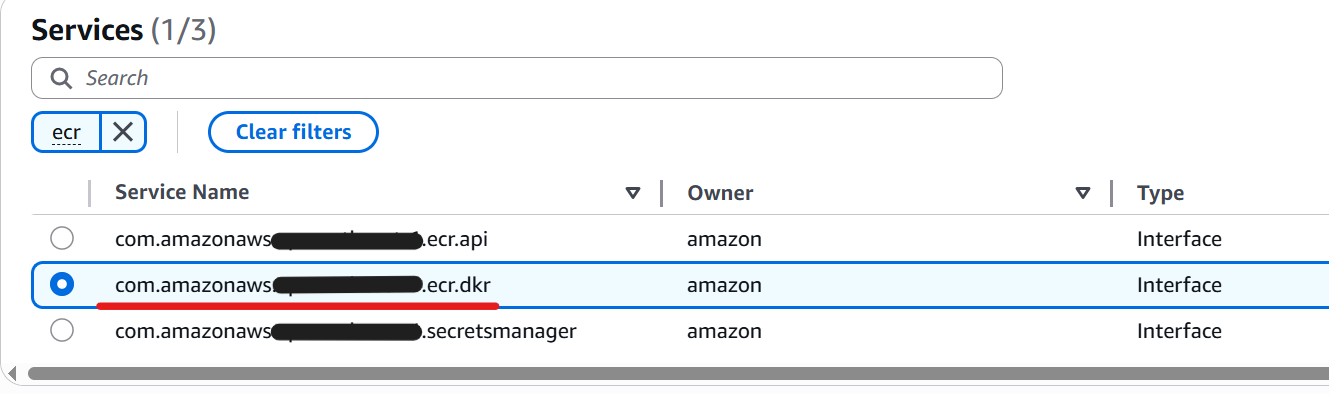
Select your VPC, private subnets and security group for private.
Click “Create endpoint”.
Repeat the same steps for the others.
9. Create Application Load Balancer
Create an Application Load Balancer to distribute incoming traffic across Fargate containers.
Go to EC2 on AWS Management Console.
Click “Load Balancers”.
Click “Create Application Load Balancer”.
Enter a Load Balancer name, choose “Internet-facing” for the Scheme, and select “IPv4” for the IP address type.
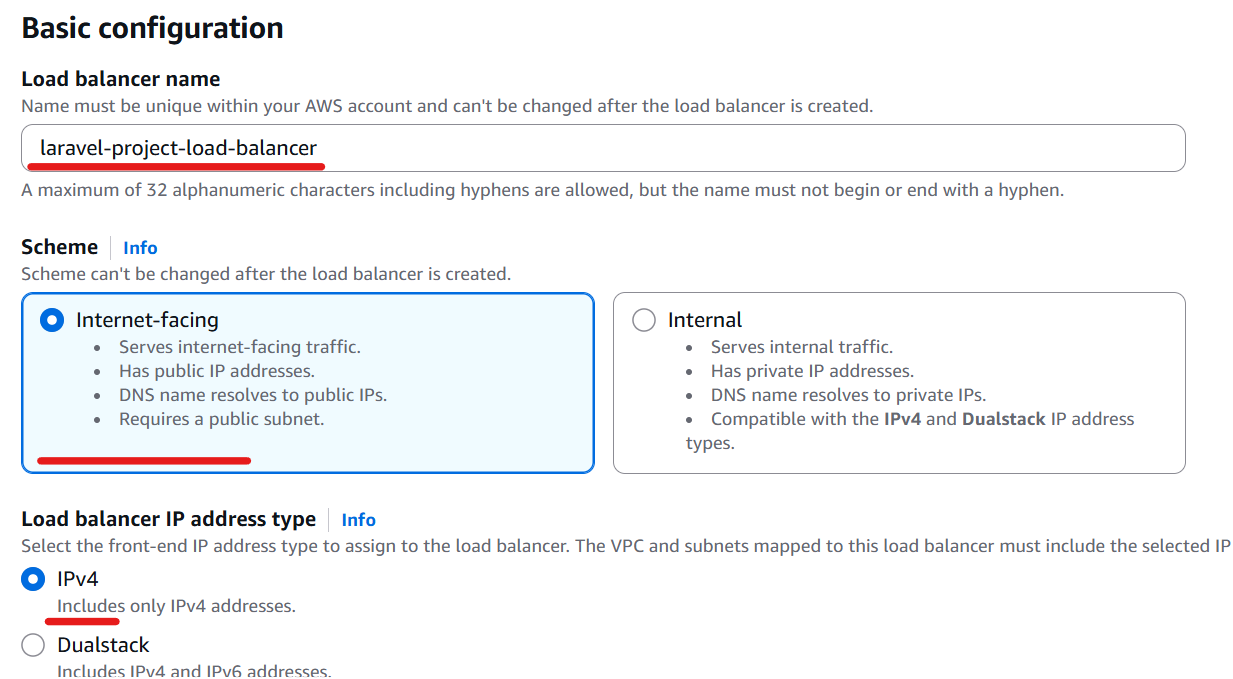
Select your VPC, public subnets and security group for public.
Then click “Create target group”.
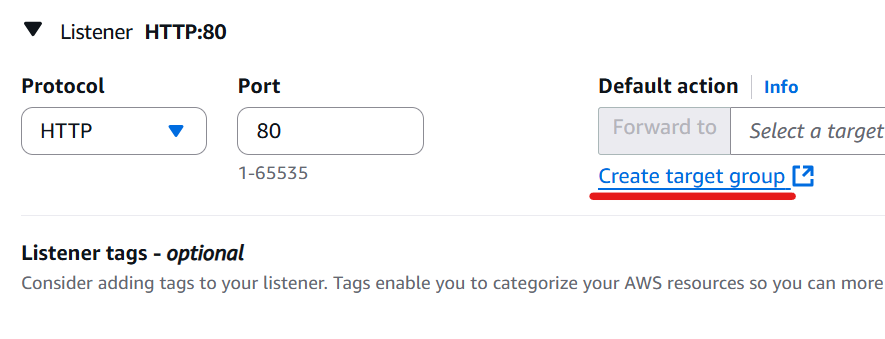
Choose “IP addresses” as the target type.
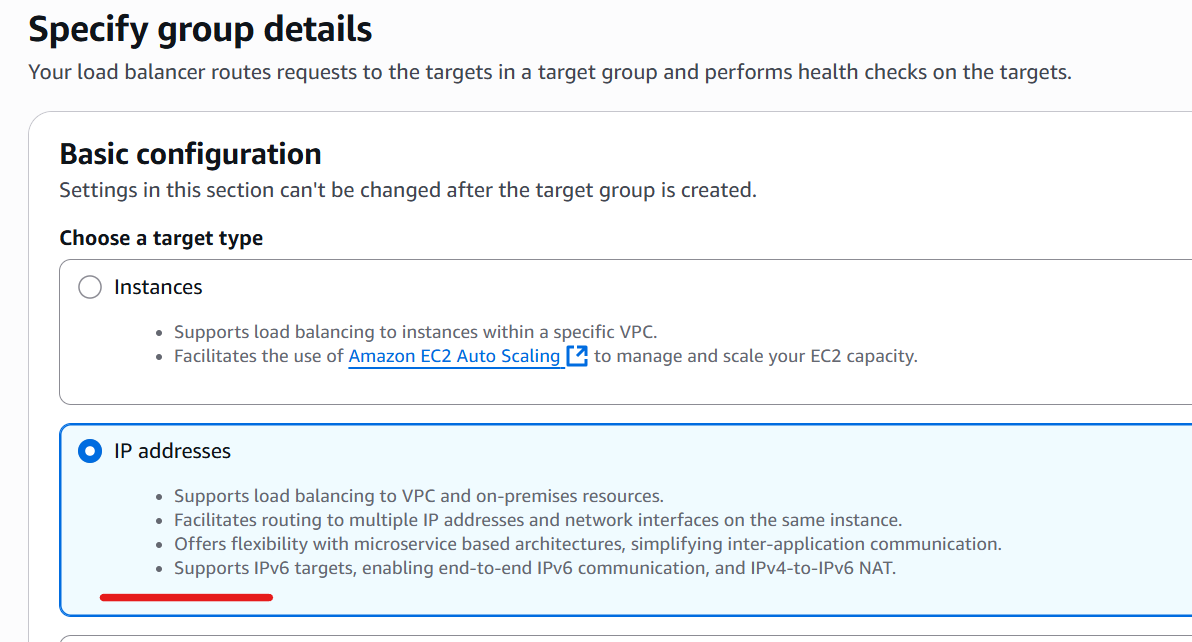
Enter “Target group name” and specify “HTTP” for the Protocol and “80” for the Port.
Select “IPv4” for the IP address type.
Select your VPC.
Configure the Health checks as follows.
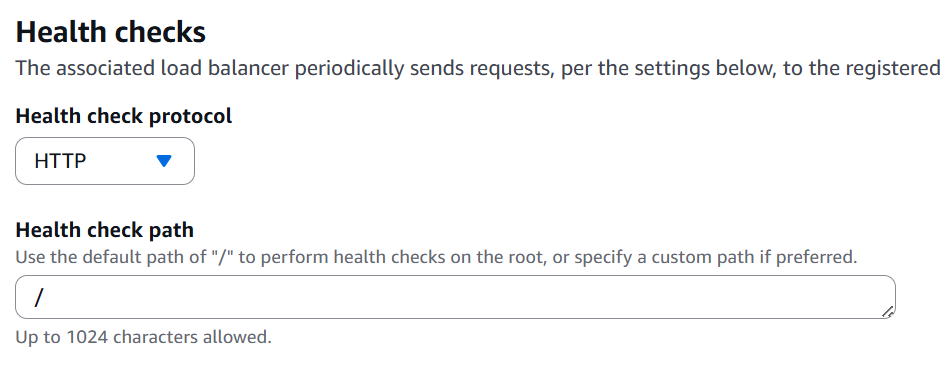
Click “Next”, then click “Create target group”.
Return to the Load Balancer creation screen.
Select the target group you just created as the listener’s target.
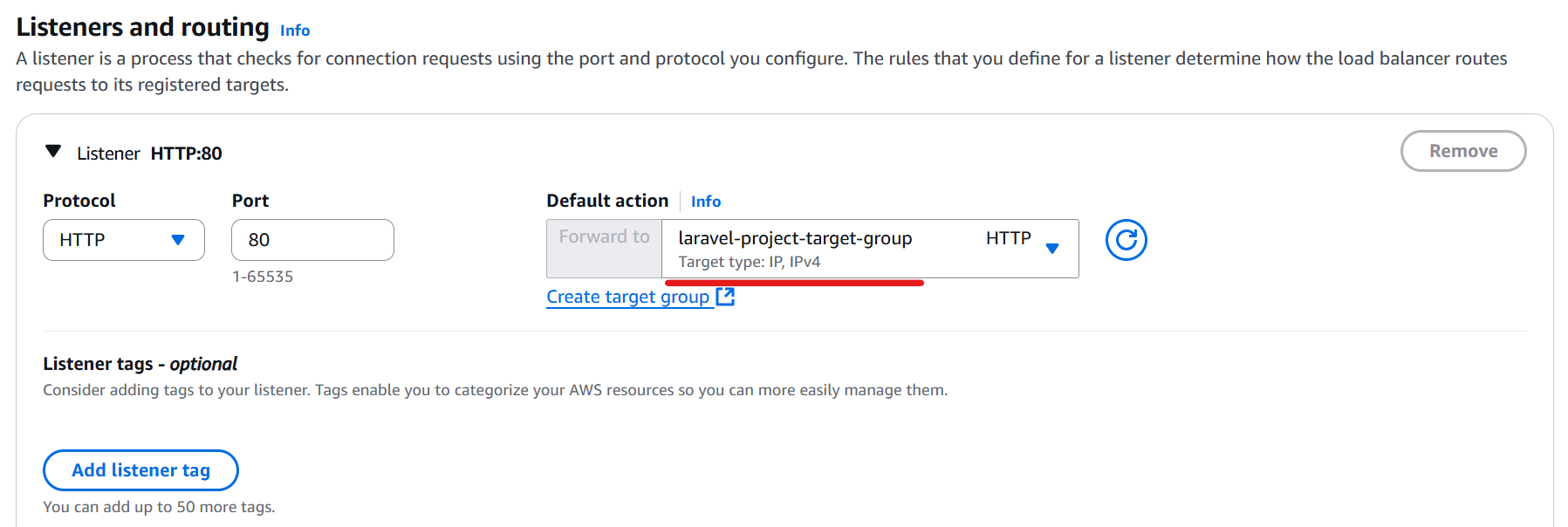
Click “Create load balancer”.
10. Create Service
Return to your clusters screen on AWS Management Console.
Click your cluster.
Click the “Create” button.
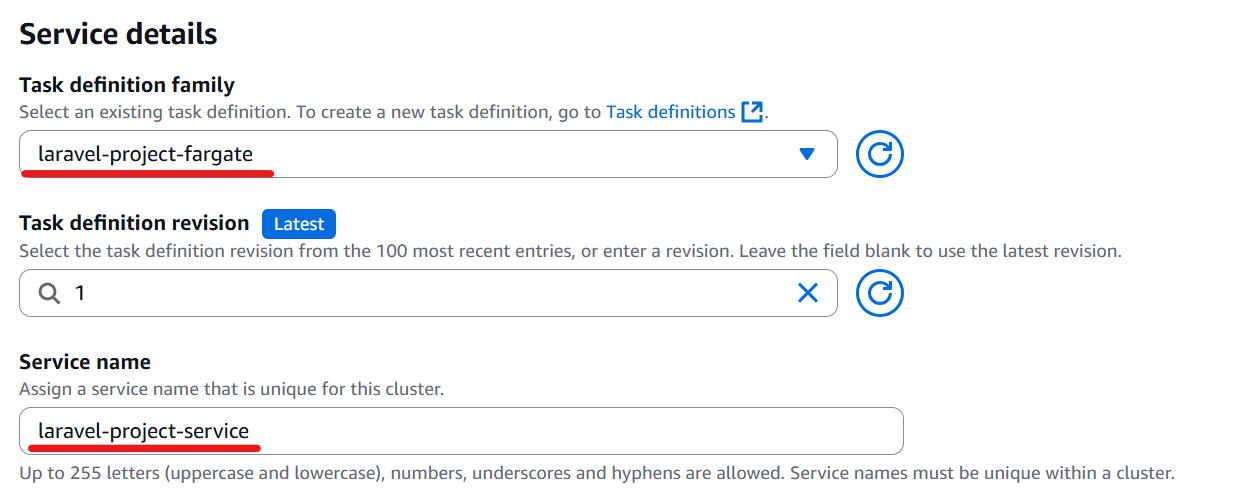
Enter the task definition family; the latest revision and service name will be populated automatically.
In this example, the service name was changed as follows.
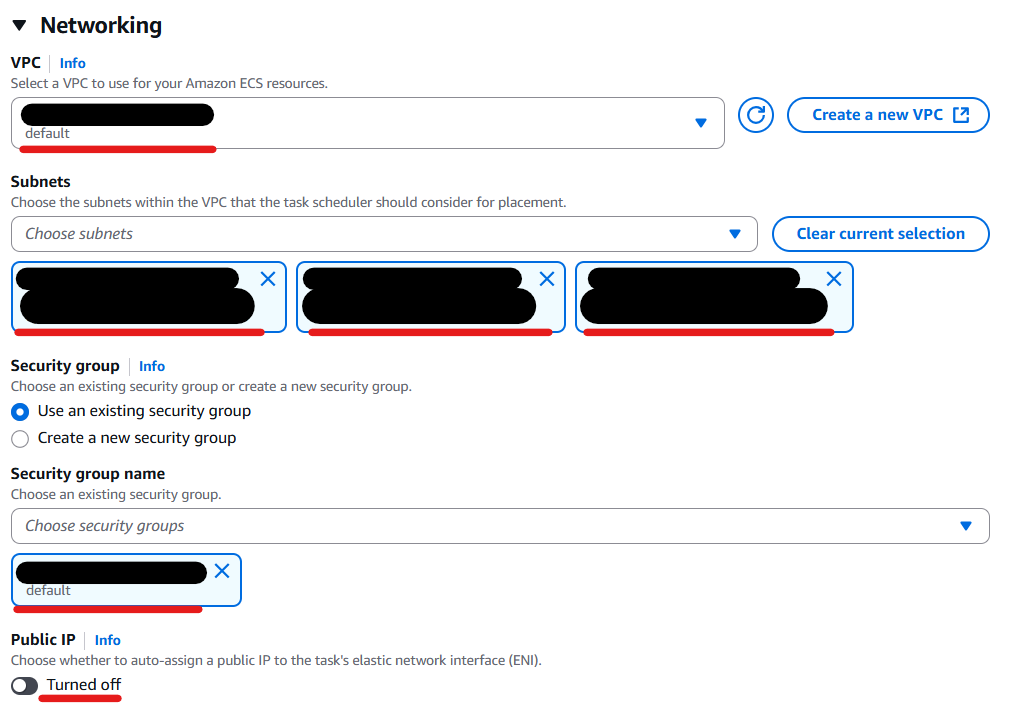
Select your VPC, private subnets and security group for private.
Then turn the “Public IP” button off.
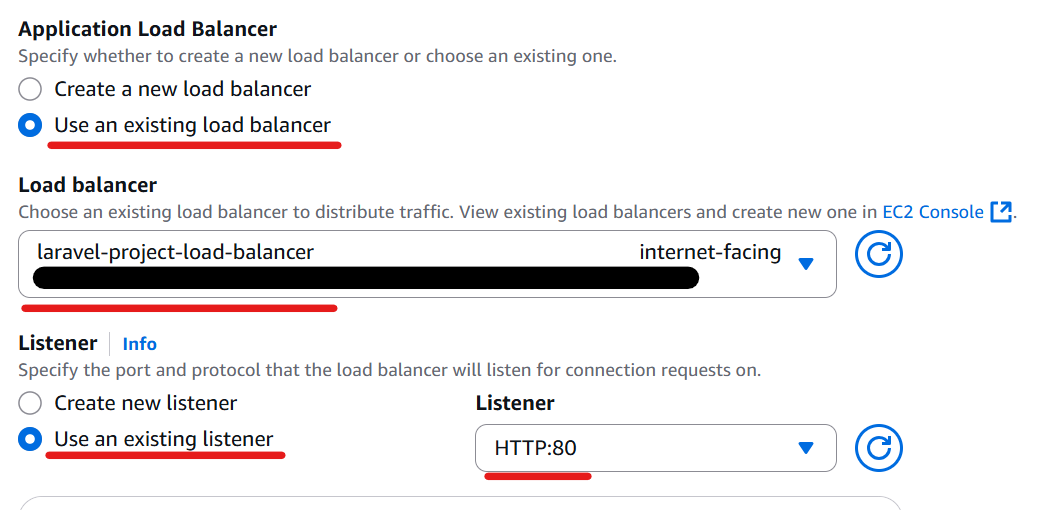
Then configure the Load balancing.
Specify the load balancer you created.
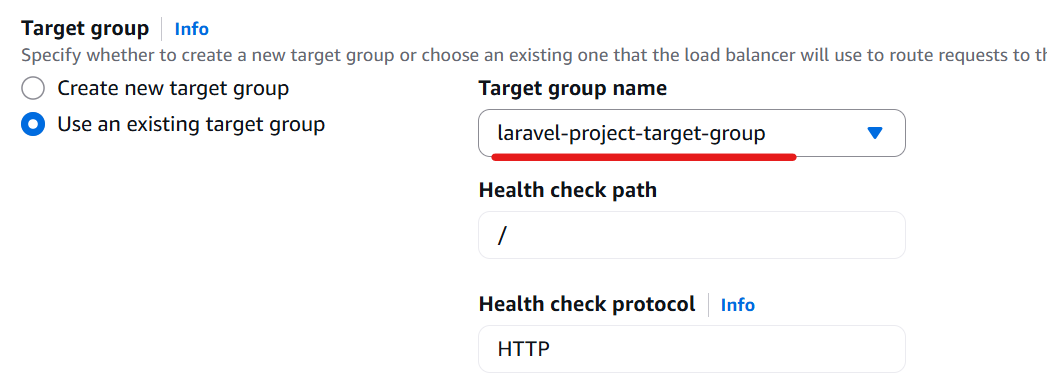
Click the “Create” button.
11. Verify Laravel Project
Retrieve the DNS name from the “Details” section of your load balancer.
Access http://<Your load balancer DNS name> in your browser (e.g. http://laravel-project-load-balancer-xxxxx.xxxxx.elb.amazonaws.com).
If you see the following web page, your Laravel project was successfully deployed to ECS.