Laravel + shadcn/ui Pagination
web-application-framework laravel
This article explains how to display Laravel pagination data using shadcn/ui.

References
Prerequisite
- You already have a Laravel project set up with React.
For more information, refer to this article.
Environment
- Windows 11
- Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS (WSL2 distribution)
- Docker Engine 28.4.0
- Amazon Linux 2023(OS of the Docker container)
- PHP 8.2.15 (fpm-fcgi)
- NGINX 1.24.0
- Laravel 12
- Node.js 20.14.0
- Vite 7.1.9
- React 19.2.0
- @inertiajs/react 2.2.6
Workflow
1. Implement Laravel Pagination
Laravel provides built-in pagination support with both the query builder and the Eloquent ORM.
In this example, we’ll use Eloquent.
Create a UserController using the Artisan command:
php artisan make:controller UserController
Next, add the pagination logic. Edit the generated controller file as follows:
UserController.php:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\User;
use Inertia\Inertia;
use Inertia\Response;
class UserController extends Controller
{
/**
* Show all application users.
*/
public function index(): Response
{
return Inertia::render('User/Index', [
'users' => User::paginate(5)
]);
}
}
According to The official documentation:
The paginate method automatically takes care of setting the query’s “limit” and “offset” based on the current page being viewed by the user.
In other words, Laravel handles the pagination logic for you.
You just need to specify how many users to display per page and implement the front-end UI.
2. Implement shadcn/ui Pagination
Run the following command to install the Pagination component from shadcn/ui:
npx shadcn@latest add pagination
After running the command, a pagination.tsx file will be created in the resources/js/components/ui directory.
Next, create a user list page using Inertia.js and shadcn/ui.
Create a file named resources/js/Pages/User/Index.tsx.
Index.tsx:
import {
Card,
CardContent,
CardHeader,
CardTitle,
} from '@/components/ui/card'
import {
Pagination,
PaginationContent,
PaginationItem,
PaginationNext,
PaginationPrevious,
} from "@/components/ui/pagination"
// Laravel pagination data structure (only the necessary properties)
type PaginationData<T> = {
data: T[],
prev_page_url: string | null,
next_page_url: string | null,
}
// Users table data structure (only displayed columns)
type User = {
name: string,
email: string,
}
export default function Index({ users }: { users: PaginationData<User>}) {
// Create pagination items based on the presence of previous and next page URLs
const prevPageLink = users.prev_page_url === null ? null : (
<PaginationItem>
<PaginationPrevious href={users.prev_page_url} />
</PaginationItem>
)
const nextPageLink = users.next_page_url === null ? null : (
<PaginationItem>
<PaginationNext href={users.next_page_url} />
</PaginationItem>
)
return (
<div>
{/* Display user data */}
{users.data.map((user, index) => (
<Card key={index}>
<CardHeader>
<CardTitle>{user.name}</CardTitle>
</CardHeader>
<CardContent>
{user.email}
</CardContent>
</Card>
))}
{/* Display pagination controls */}
<Pagination>
<PaginationContent>
{prevPageLink}
{nextPageLink}
</PaginationContent>
</Pagination>
</div>
)
}
If you don’t have the Card component from shadcn/ui, install it as follows:
npx shadcn@latest add card
The users pagination response includes the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| current_page | The current page number. |
| data | The data list retrieved from the database. |
| first_page_url | The first page URL. |
| from | The starting item number. |
| last_page | The total number of pages. |
| last_page_url | The last page URL. |
| links | The page links for navigation. |
| next_page_url | The next page URL. |
| path | The base URL of the current page. |
| per_page | The number of items displayed per page. |
| prev_page_url | The previous page URL. |
| to | The ending item number. |
| total | The total number of items. |
3. Verify Pagination
Add a route in the routes/web.php file:
web.php:
Route::get('/users', [UserController::class, 'index']);
Open the /users page in your browser.
You should see a page like this:
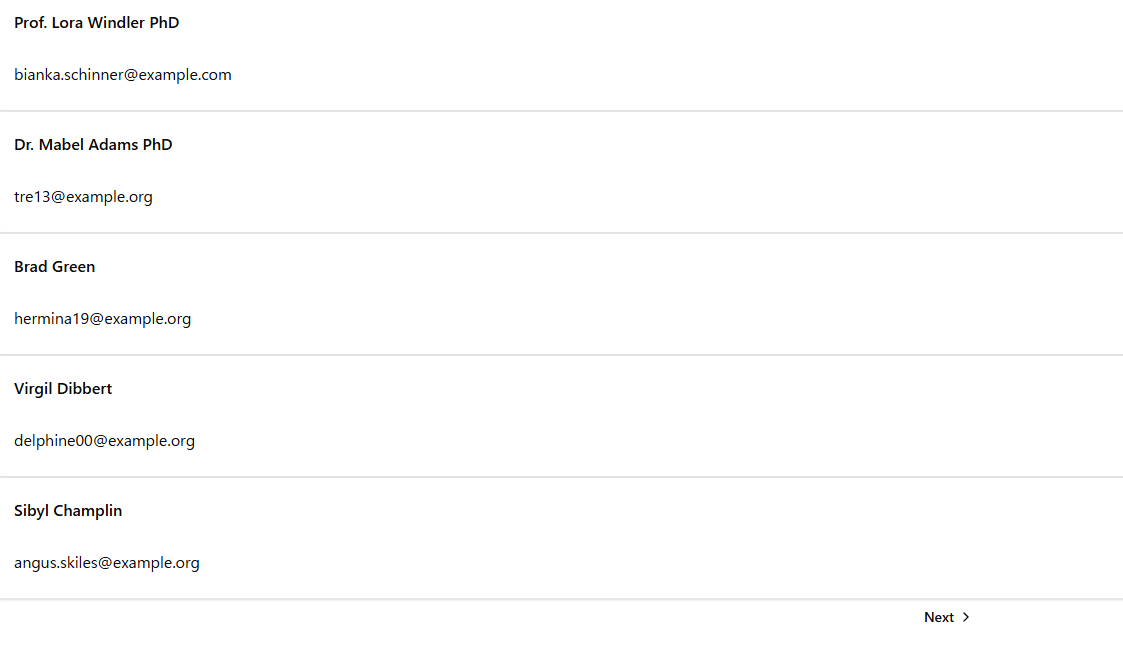
Clicking the Next button should display the second page:
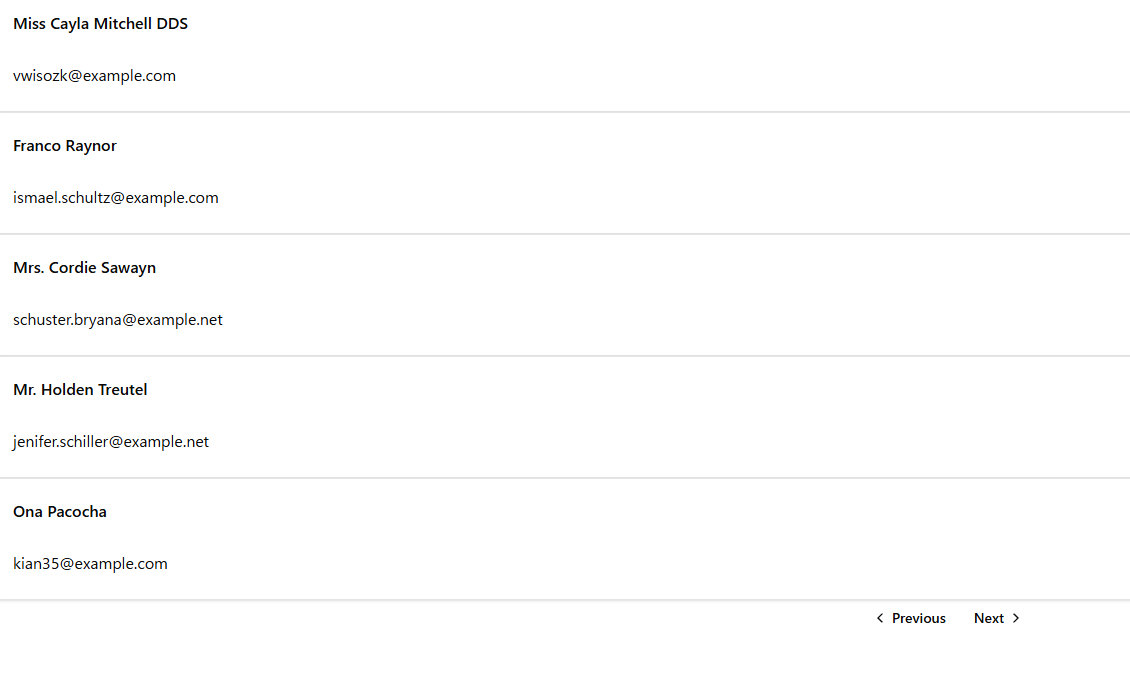
(Bonus) Other Paginate Methods
Laravel provides several other pagination methods.
simplePaginate
As the official documentation explains, the paginate method counts the total number of matching records before retrieving them from the database.
If you don’t need the total record count, you can use simplePaginate instead for better performance.
User::simplePaginate(5)
This method returns the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| current_page | The current page number. |
| current_page_url | The current page URL. |
| data | The data list retrieved from the database. |
| first_page_url | The first page URL. |
| from | The starting item number. |
| next_page_url | The next page URL. |
| path | The base URL of the current page. |
| per_page | The number of items displayed per page. |
| prev_page_url | The previous page URL. |
| to | The ending item number. |
cursorPaginate
As noted in the official documentation, the cursorPaginate method is the most efficient way to handle pagination.
While paginate and simplePaginate create queries using the SQL “offset” clause, cursor pagination works by constructing “where” clauses that compare the values of the ordered columns contained in the query, providing the most efficient database performance available amongst all of Laravel’s pagination methods.
The difference between “offset” and “cursor” pagination can be illustrated as follows (adapted from this page):
# Offset pagination
select * from users order by id asc limit 15 offset 15;
# Cursor pagination
select * from users where id > 15 order by id asc limit 15;
The response includes the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| data | The data list retrieved from the database. |
| next_cursor | The next cursor value. |
| next_page_url | The next page URL. |
| path | The base URL of the current page. |
| per_page | The number of items displayed per page. |
| prev_cursor | The previous cursor value. |
| prev_page_url | The previous page URL. |
Related articles
- How to Fix “Permission denied: laravel.log” Error (Laravel)
- How to Generate and Display QR Codes with Laravel and React (qrcode.react)
- How to Run Code After a Successful Stripe Payment Using Webhooks
- Install Laravel Cashier (Stripe)
- Why the 419 Error Is Thrown When Using Fetch in Laravel?
- Laravel + shadcn/ui Pagination
- Interacting with PostgreSQL from a Laravel Project
- Inertia.js + shadcn/ui Form on Laravel
- Set Up Laravel with a React Project
- Install Bootstrap in a Laravel Project