How to Set Up a NestJS + Nginx Reverse Proxy with Docker Compose
web-application-framework nestjs
In this article, we’ll set up a NestJS + Nginx environment using a reverse proxy with Docker Compose.
This project uses Amazon Linux as the base image to align with AWS environments and to allow flexible OS-level customization.
While official Node.js or Nginx images are commonly used in production, this setup reflects a more infrastructure-oriented approach.

References
Environment
- Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS (WSL2 distribution)
- Docker Engine 28.4.0
- Amazon Linux 2023(OS of the Docker container)
- Node.js 24.13.1
- NestJS 11.0.1
- NGINX 1.28.2
Setup Steps
- Create a NestJS Project
- Create Configuration Files
- Create Docker Configuration Files
- Check the NestJS Project
1. Create a NestJS Project
First, start a Docker container to create a NestJS project.
Run the following commands:
$ cd <path-to-nestjs-project-dir>
$ docker run -it --rm --name node_to_install_nestjs -w /app -v `pwd`:/app node:24.13.1 bash
This command starts a container named node_to_install_nestjs from the node:24.13.1 image and connects to it using bash.
Install the NestJS CLI and create your project.
Inside the container, run:
$ npm i -g @nestjs/cli
$ nest new <project-name>
Replace <project-name> with your desired project name.
If successful, the NestJS project will be created in the current directory.
To confirm, run:
$ ls
<project-name>
Since the docker run command used the -v option to mount the host directory into the container, the project is also visible from the host system.
You can check from the host like this:
$ exit # Exit the container
$ ls
<project-name>
2. Create Configuration Files
Create the following configuration files within your NestJS project directory.
In this explanation, the current directory refers to the project root.
nginx.repo
This configuration file sets up a YUM repository for Amazon Linux 2023.
It is based on the official Nginx installation guide for Amazon Linux 2023.
Create this file in the docker/web/nginx directory.
docker/web/nginx/nginx.repo :
[nginx-stable]
name=nginx stable repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/amzn/2023/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
[nginx-mainline]
name=nginx mainline repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/amzn/2023/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
module_hotfixes=true
default.conf
Create the Nginx configuration file for the NestJS project in the docker/web/nginx/conf.d directory.
docker/web/nginx/conf.d/default.conf :
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
NestJS starts a server listening on the port defined in the src/main.ts file (the default is 3000).
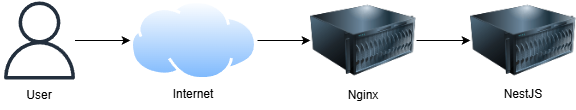
In this configuration, Nginx acts as a reverse proxy.
When a user sends a request to the application, Nginx receives it and forwards it to the NestJS application.
3. Create Docker Configuration Files
Create the following Docker-related configuration files.
In this explanation, the current directory refers to the project root.
docker-compose.yml
This is the Docker Compose configuration file.
Create it in the project root directory.
docker-compose.yml :
services:
web:
build: ./docker/web
volumes:
- .:/srv/example.com
ports:
- "8080:80"
command: bash -c "chmod 755 /srv/example.com/docker/web/start.sh &&
/srv/example.com/docker/web/start.sh"
Dockerfile
This Dockerfile defines the web service (Nginx + Node.js).
We use the amazonlinux base image with future AWS deployment in mind.
Create it in the docker/web directory.
docker/web/Dockerfile :
FROM amazonlinux:2023
# Install Nginx
RUN yum -y install yum-utils
COPY nginx/nginx.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
RUN yum -y install nginx-1.28.2
COPY nginx/conf.d/default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
# Install Node.js
RUN yum -y install tar
RUN touch ~/.bashrc
COPY install-npm.sh /tmp/install-npm.sh
RUN chmod 755 /tmp/install-npm.sh
RUN /tmp/install-npm.sh 24.13.1
install-npm.sh
Create install-npm.sh to install Node.js and npm.
Place it in the docker/web directory.
docker/web/install-npm.sh:
#!/bin/bash
set -euxo pipefail
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.40.3/install.sh | bash
source ~/.bashrc
VERSION=$1
nvm install $VERSION
start.sh
Create start.sh which runs when the Docker container starts.
Place it in the docker/web directory.
docker/web/start.sh:
#!/bin/bash
set -euxo pipefail
# Add the nginx user to the root group for permission access.
usermod -aG root nginx
# Load nvm and install npm packages
cd /srv/example.com
source ~/.bashrc
npm ci
# Start Nginx
# By using -g "daemon off;", Nginx runs in the foreground, preventing the container from exiting automatically.
nginx -g "daemon off;"
4. Check the NestJS Project
Start the Docker container:
$ cd <path-to-your-nestjs-project-root>
$ docker compose up --build -d
Start the NestJS server inside the container:
$ docker compose exec web bash # Connect to the container
$ cd /srv/example.com
$ npm run start
Access the application in your browser: http://localhost:8080

If everything works correctly, you should see the Hello World! message.