Automated Deployment to ECS Using GitHub Actions
This article explains how to automate deployment to Amazon ECS on AWS using GitHub Actions.
Reference
- Deploying to Amazon Elastic Container Service
- Configuring OpenID Connect in Amazon Web Services
- Configuring a role for GitHub OIDC identity provider
- GitHub Actions から AWS へアクセスする
Prerequisites
- An AWS account
- A user in IAM Identity Center
For more information, follow this instruction. - A GitHub repository
Environment
- Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS (running on WSL)
- Docker Engine 26.0.0
- Laravel 11
Deployment Steps
- Deploy a Project
- Create an OIDC Identity Provider
- Create a Role for GitHub OIDC Identity Provider
- Add Role to Assume to Repository Secrets
- Create a Task Definition in Your Repository
- Create a Workflow
- Verify the Workflow
1. Deploy a Project
Deploy your project to ECS.
For details, refer to this guide.
2. Create an OIDC Identity Provider
OpenID Connect (OIDC) is used for authentication with AWS.
Here’s an explanation from this page.
OpenID Connect (OIDC) allows your GitHub Actions workflows to access resources in Amazon Web Services (AWS), without needing to store the AWS credentials as long-lived GitHub secrets.
To create an OIDC identity provider, go to IAM on the AWS Management Console.
Click “Identity providers”.
Click “Add provider”.

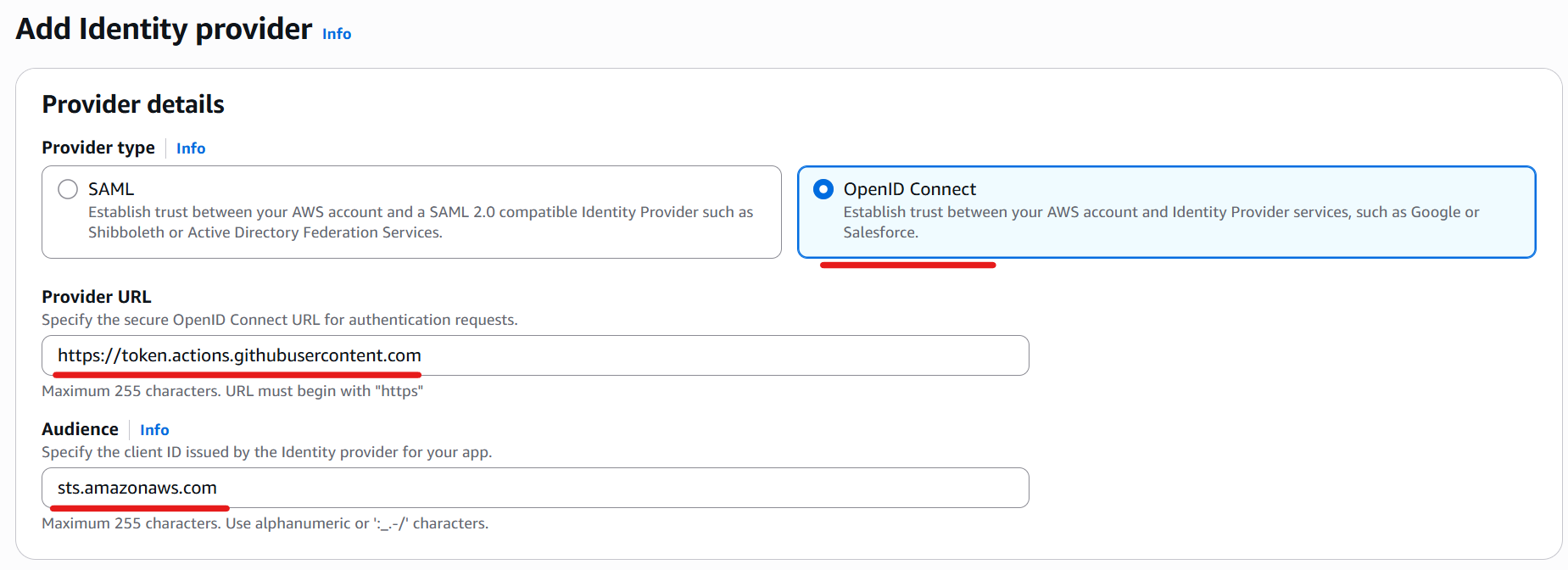
Select “OpenID Connect” and enter the following values, as provided in this documentation.
| Provider URL | https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com |
| Audience | sts.amazonaws.com |
3. Create a Role for GitHub OIDC Identity Provider
Go to “Role” on IAM on the AWS Management Console.
Click “Create role”.

Select “Web identity”.
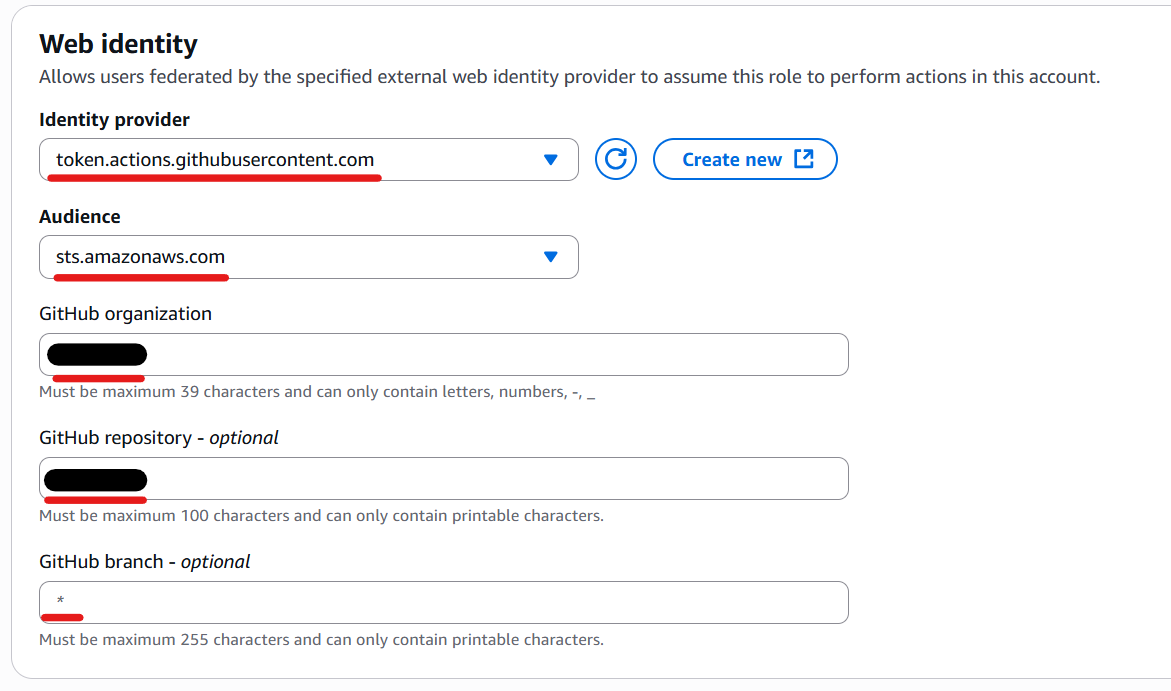
Fill in the following fields, then click “Next”.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Identity provider | The OIDC identity provider you created. |
| Audience | The audience you specified. |
| GitHub organization | Your GitHub user name. |
| GitHub repository | The repository name(s) this role will be used for. Use * for all repositories. |
| GitHub branch | The branch name(s) this role will be used for. Use * for all branches. |
Click “Next” on the “Add permission” screen.
Enter a role name and description, then click “Create role”.
Attach required policies for ECR, ECS and IAM.
Click the role you just created on IAM on the AWS Management Console.
Click “Create inline policy”.
Switch to the JSON tab, then enter the following policy.
For ECR:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:BatchGetImage",
"ecr:CompleteLayerUpload",
"ecr:UploadLayerPart",
"ecr:InitiateLayerUpload",
"ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability",
"ecr:PutImage"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:ecr:<Your repository region>:<Your Account ID>:repository/<Your repository name>"
},
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "ecr:GetAuthorizationToken",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Click “Next”, then enter a policy name.
Click “Create policy”.
Repeat the same steps for ECS and IAM.
For ECS:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecs:UpdateService",
"ecs:RegisterTaskDefinition",
"ecs:DescribeServices"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:ecs:<Your cluster region>:<Your Account ID>:service/<Your cluster name>/*",
"arn:aws:ecs:<Your cluster region>:<Your Account ID>:task-definition/<Your task definition name>:*"
]
}
]
}
For IAM:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:PassRole",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::<Your Account ID>:role/<Your task execution role name>"
}
]
}
4. Add Role to Assume to Repository Secrets
Go to your GitHub repository and click “Settings”.
Click “Secrets and Variables” > “Actions”.
Click “New repository secret”.
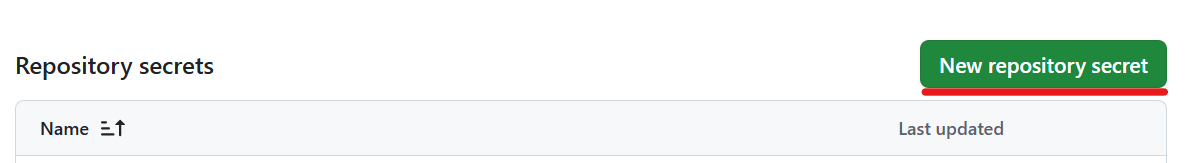
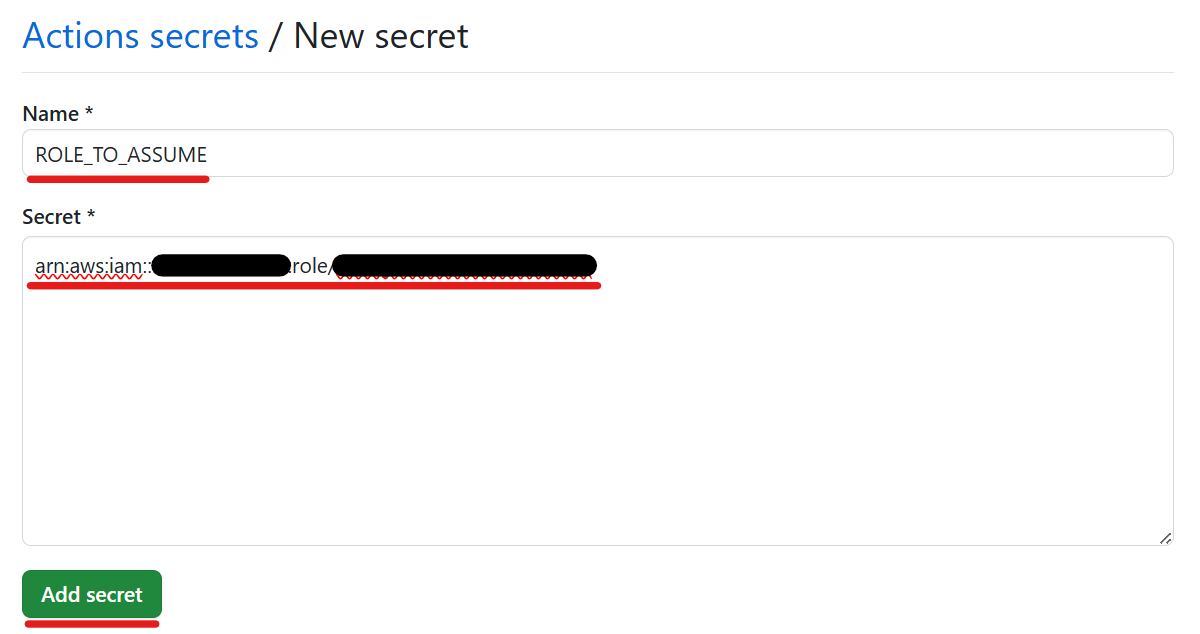
Enter a name (e.g. ROLE_TO_ASSUME) and paste your role ARN as the secret value.
Click “Add secret”.
5. Create a Task Definition in Your Repository
Create a task definition JSON file in your repository.
For example, save it as .aws/task-definition.json.
6. Create a Workflow
Go to “Actions” on your GitHub repository.
Click “New workflow”.
Click “Configure” of “Deploy to Amazon ECS”.
This workflow builds a Docker image and push it to ECR.
Then it replaces “image” in the task definition with new one and deploys the task definition to ECS.
Update the environment variables with your actual values in the YAML file.
AWS_REGION: MY_AWS_REGION # set this to your preferred AWS region, e.g. us-west-1
ECR_REPOSITORY: MY_ECR_REPOSITORY # set this to your Amazon ECR repository name
ECS_SERVICE: MY_ECS_SERVICE # set this to your Amazon ECS service name
ECS_CLUSTER: MY_ECS_CLUSTER # set this to your Amazon ECS cluster name
ECS_TASK_DEFINITION: MY_ECS_TASK_DEFINITION # set this to the path to your Amazon ECS task definition
# file, e.g. .aws/task-definition.json
CONTAINER_NAME: MY_CONTAINER_NAME # set this to the name of the container in the
# containerDefinitions section of your task definition
Add id-token: write to permissions for OIDC.
permissions:
id-token: write # Add
contents: read
Update “Configure AWS credentials” to use ROLE_TO_ASSUME.
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1
with:
role-to-assume: ${{ secrets.ROLE_TO_ASSUME }} # Add
aws-region: ${{ env.AWS_REGION }}
If your Dockerfile isn’t in the root directory, specify the -f option in the docker build command.
Example:
docker build -t $ECR_REGISTRY/$ECR_REPOSITORY:$IMAGE_TAG -f ./docker/web/Dockerfile .
Enter a file name (e.g. aws.yml) and click “Commit changes”.
This workflow will run because it’s triggered when changes are pushed to the “main” branch.
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
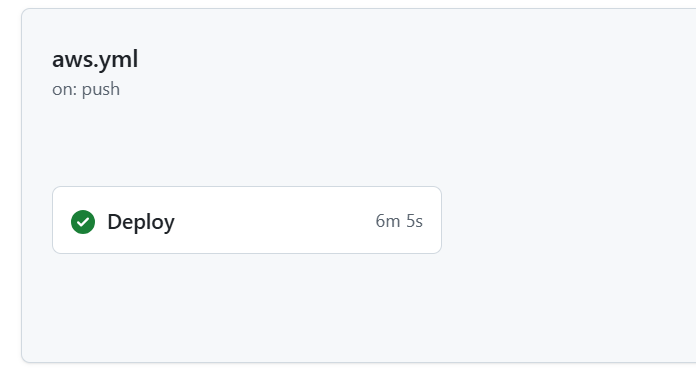
7. Verify the Workflow
Go to “Actions” on your GitHub repository.

If you see a successful run like the following, the workflow has completed successfully.