How to Access External Services from a Private ECS Fargate Container (NAT Gateway)
This article explains how to access external services from a private ECS Fargate container via a NAT Gateway.

Prerequisite
- Your project is already deployed to ECS
For more information, follow this instruction.
Workflow
1. Create NAT Gateway
Go to NAT Gateways on AWS Management Console.
Click “Create NAT Gateway”.
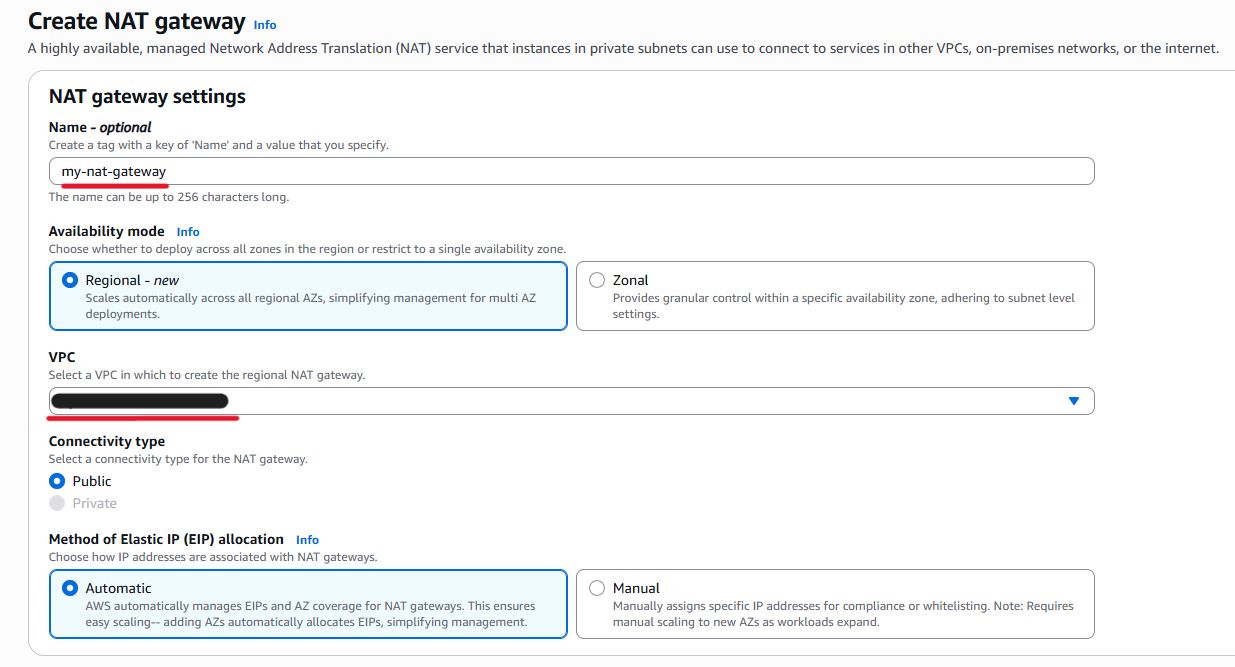
Enter a name and select your VPC.
“Regional” is set to “Availability mode” by default. If you need to set it up for a specific availability zone, select “Zonal” and configure it accordingly.
Also, “Automatic” is already set to “Method of Elastic IP (EIP) allocation”. Select “Manual” if you want to use Elastic IP addresses that you prepared in advance.
Make sure “Connectivity type” is “Public”.
Then Click “Create NAT Gateway”.
2. Edit Private Route Table
Go to Route tables on AWS Management Console.
Select your private route table and click “Edit routes”.
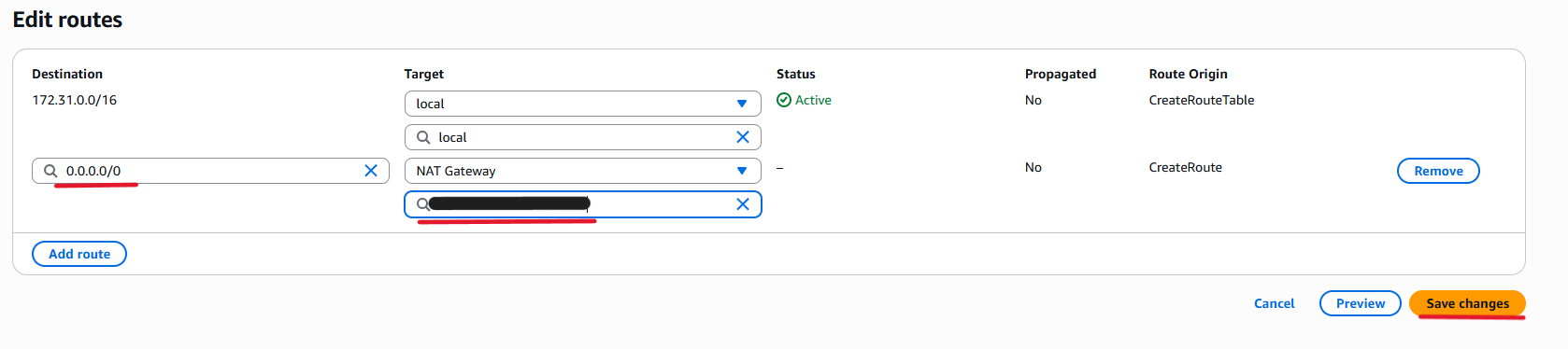
Add the following route and click “Save changes”.
This configuration sends all outbound traffic to the internet via the NAT Gateway.
| Destination | Target |
|---|---|
| 0.0.0.0/0 | NAT Gateway (created above) |
With this setup, private ECS containers can access external services such as external APIs, Amazon S3, and other AWS services. Note: For AWS services such as Amazon S3, using a VPC Endpoint is recommended instead of a NAT Gateway.